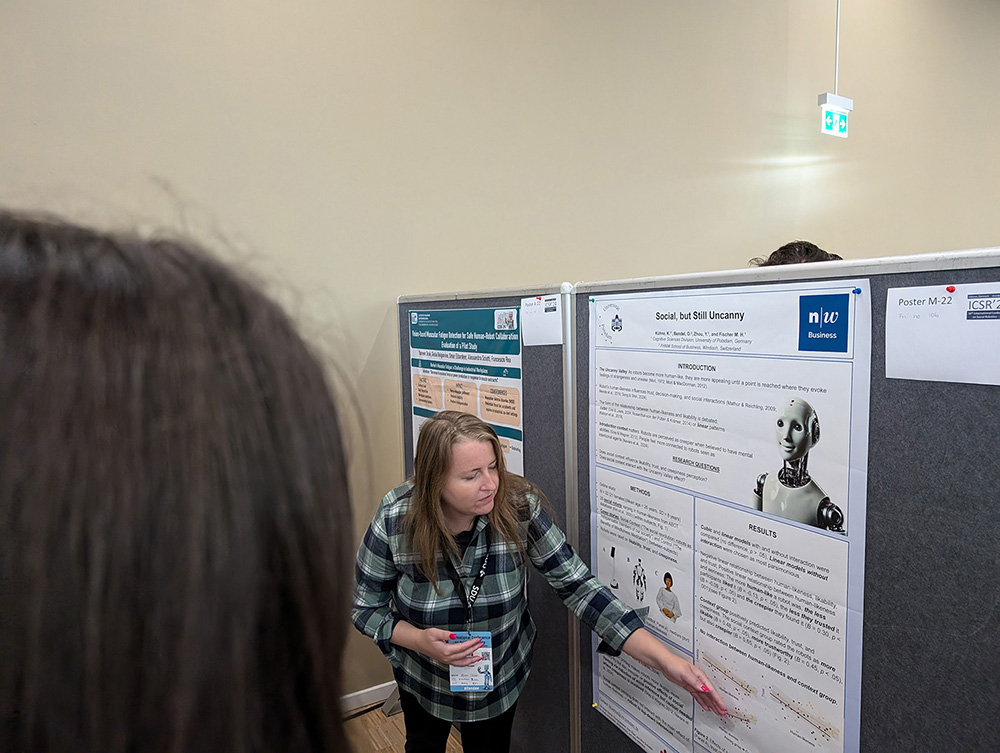
The uncanny valley effect is a famous hypothesis. Whether it can be influenced by context is still unclear. In an online experiment, Katharina Kühne and her co-authors Oliver Bendel, Yuefang Zue, and Martin Fischer found a negative linear relationship between a robot’s human likeness and its likeability and trustworthiness, and a positive linear relationship between a robot’s human likeness and its uncaniness. “Social context priming improved overall likability and trust of robots but did not modulate the Uncanny Valley effect.” (Abstract) Katharina Kühne outlined these conclusions in her presentation “Social, but Still Uncanny” – the title of the paper – at the International Conference on Social Robotics 2024 in Odense, Denmark. Like Yuefang Zue and Martin Fischer, she is a researcher at the University of Potsdam. Oliver Bendel teaches and researches at the FHNW School of Business. Together with Tamara Siegmann, he presented a second paper at the ICSR.
Testing the Uncanny Valley Effect
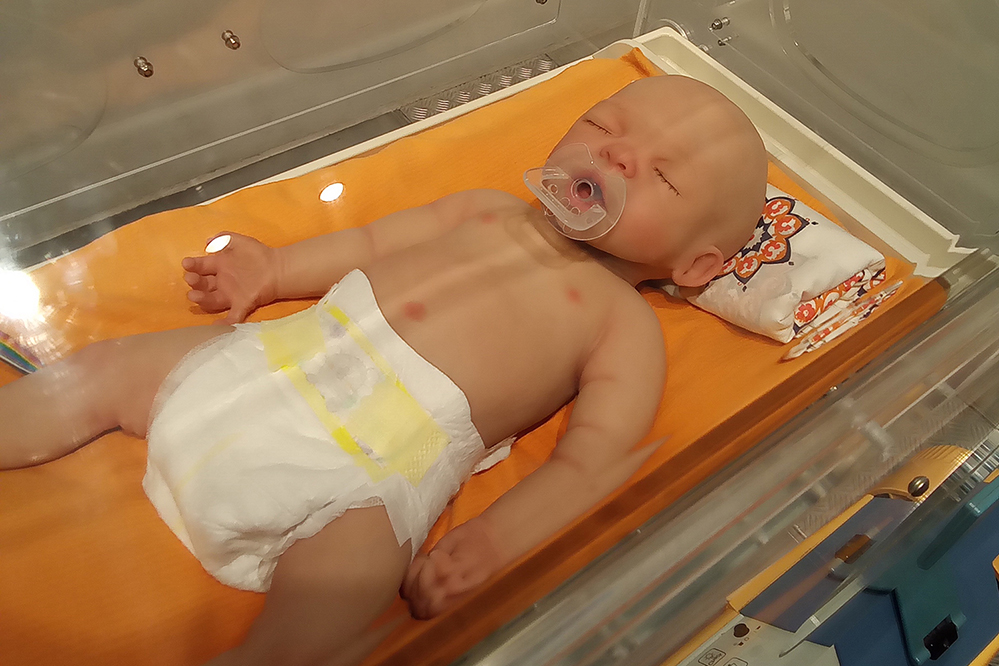
The Copernicus Science Centre’s exhibition “The Future is Now” helps to face and understand the challenges of today’s world in all its complexity. “It shows different technological solutions and encourages to look at them in a critical way. It also takes notice of the relationships between our personal values and the values of others.” (CSC website) The exhibition is divided into three parts. Two of them can already be visited: “Digital Brain?” and “Mission: Earth”. The last part (“Human 2.0”) is scheduled to open on 15 October 2024. Part of the “Digital Brain” (“#Relationships”) is BABYCLON, a robotic baby (Photo: Katharina Kühne). According to the organizers, this will allow visitors to test the uncanny valley effect on themselves. “Are we ready to meet our machine lookalikes? Not really. It turns out that the more indistinguishable from humans a robot is, the weirder feelings it evokes. See for yourself if the ‘uncanny valley’ effect works on you.” (CSC website) This is not exactly what the uncanny valley thesis means. It is about very high expectations of very human-like robots, which are then disappointed by, for example, Sophie’s weird smile or BABYCLON’s strange behavior. More information at www.kopernik.org.pl/en/education-and-information-campaigns/exhibition-future-today.
Ameca’s Smile
UK-based company Engineered Arts showed off one of its creations in a YouTube video in late 2021. The humanoid robot Ameca makes a series of fascinating human-like facial expressions. The Verge magazine describes this process: “At the start of the video, Ameca appears to ‘wake up,’ as its face conveys a mix of confusion and frustration when it opens its eyes. But when Ameca starts looking at its hands and arms, the robot opens its mouth and raises its brows in what it looks like is amazement. The end of the video shows Ameca smiling and holding a welcoming hand out towards the viewer – if that’s how you want to interpret that gesture.” (The Verge, 5 December 2021) However, this smile does not turn out perfectly – a problem that affects all androids. Almost every emotional movement can now be simulated well – except for the one whose expression is the smile. Only when this problem is solved will Sophia, Erica, and Ameca be able to get out of Uncanny Valley (Photo: Engineered Arts, from the YouTube Video).