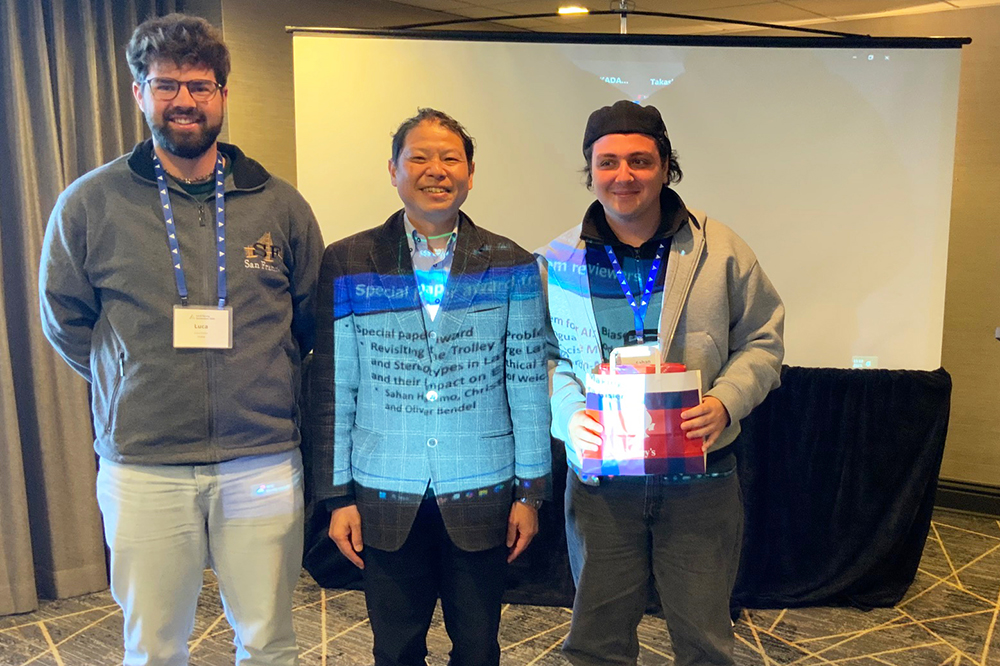
The paper “Revisiting the Trolley Problem for AI: Biases and Stereotypes in Large Language Models and their Impact on Ethical Decision-Making” by Şahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, Luca Gisler, and Oliver Bendel received the Special Paper Award from the reviewers of the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposium “Human-Compatible AI for Well-being: Harnessing Potential of GenAI for AI-Powered Science”. The three bachelor students from the FHNW School of Computer Science gave their presentation on site in San Francisco as part of the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposia. Prof. Dr. Bendel from the FHNW School of Business had given them feedback on the project and placed it in the context of machine ethics. He has been involved in the well-known and popular conference, which usually takes place at Stanford University, since 2016. This time, he was keeping his fingers crossed from Italy. The proceedings of the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposia will be published shortly.
About Inclusive AI
The Gabler Wirtschaftslexikon is the largest economics encyclopedia in the German-speaking world. In March 2025, Oliver Bendel published an article on inclusive AI in this reference work. The first part reads as follows: “Inclusive AI aims, on the one hand, to combat phenomena in artificial intelligence (AI) that have an exclusionary character – such as bias, hallucination, hate speech, and deepfakes – and, on the other hand, to strengthen applications with an inclusionary character in order to support those affected. One meaning is associated with terms like “responsible AI”, “explainable AI”, and “trustworthy AI”, while the other aligns with concepts such as “AI for good” or “AI for wellbeing”. Overall, this falls under the umbrella of “ethical AI”, though this term is also used in marketing contexts. In 2025, the World Economic Forum (WEF) pointed to the digital divide, asking: “How do we ensure that the growth of AI doesn’t leave people behind and is truly inclusive?” Inclusive AI can be associated with generative AI as well as with other forms of artificial intelligence.” The full article is available at:
wirtschaftslexikon.gabler.de/definition/inclusive-ai-171870.
The VISUAL Project
The VISUAL project will be launched in March 2025 at the FHNW School of Business. It was initiated by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel. VISUAL stands for “Virtual Inclusive Safaris for Unique Adventures and Learning”. There are webcams all over the world showing wild animals. Sighted people can use them to go on photo safaris from the comfort of their sofa. Blind and visually impaired people are at a disadvantage. As part of inclusive AI – a movement that includes apps like Be My Eyes with the Be My AI feature – a solution is to be found for them. The project aims to develop a prototype by August 2025 that will allow blind and visually impaired people to have webcam images of wildlife described to them. The system takes regular snapshots of the videos and analyzes and evaluates them using a multimodal LLM. It presents the results ini spoken language via an integrated text-to-speech engine. As a byproduct, poaching, bush and forest fires, and other events can be detected. The project is likely to be one of the first to combine inclusive AI with new approaches of animal-computer interaction (ACI).
Biases and Stereotypes in LLMs
The paper “Revisiting the Trolley Problem for AI: Biases and Stereotypes in Large Language Models and their Impact on Ethical Decision-Making” by Sahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, Luca Gisler (FHNW School of Computer Science), and Oliver Bendel (FHNW School of Business) was accepted at the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposium “Human-Compatible AI for Well-being: Harnessing Potential of GenAI for AI-Powered Science”. A year ago, Sahan Hatemo had already dedicated himself to the topic of “ETHICAL DECISION MAKING OF AI: An Investigation Using a Stereotyped Persona Approach in the Trolley Problem” in a so-called mini-challenge in the Data Science degree program. His supervisor, Oliver Bendel, had told the other scientists about the idea at the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposium “Impact of GenAI on Social and Individual Well-being” at Stanford University. This led to a lively discussion. The student recruited two colleagues, Christof Weickhardt and Luca Gisler, and worked on the topic in a much more complex form in a so-called Challenge X. This time, three different open-source language models were applied to the trolley problem. In each case, personalities were created with nationality, gender, and age. In addition, the data was compared with that of the MIT Moral Machine project. Sahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, and Luca Gisler will present their results at the end of March or beginning of April 2025 in San Francisco, the venue of this year’s event.
Androids for Different Areas of Application
RealDollX and Realbotix have been known for years for Harmony, one of the most advanced sex robots in the world, known not least for the movie “Hi, AI”. Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel was able to meet and talk to the robot head at a workshop in 2019. GPT was used, as explained by Kino Coursey from Realbotix, who was present and co-developed Harmony. Oliver Bendel was able to persuade him to write the article “Speaking with Harmony“, which was published in his book “Maschinenliebe” in 2020. Realbotix has since broadened its focus. The company develops social robots – mainly female androids, but also male models – for interactive presentations, among other things. Movable arms and hands are used for this. The company’s new flagship is Aria, which caused a stir at a trade fair in 2024. The movable arms and hands could also benefit Harmony, for example when hugging. Above all, however, it enables gestures that support the already convincing facial expressions. In future, the speech capabilities of the general models will be created using several speech models. Further developments will be discussed at a meeting in March 2025, for which the teams from Texas, Nevada, and California will come together in one place (Photo: Realbotix).
kAIxo says “kaixo”
The final presentation of the “kAIxo” project took place on January 9, 2025. Nicolas Lluis Araya was the project team member. The FHNW School of Business has been developing chatbots for dead, endangered, and extinct languages for several years. A well-known example is @llegra, a chatbot for Vallader. In the spring of 2024, Oliver Bendel tested the reach of GPTs for endangered languages such as Irish (Irish Gaelic), Maori, and Basque. According to ChatGPT, there is a relatively large amount of training material for them. On May 12, 2024 – after Irish Girl and Maori Girl – a first version of Adelina, a chatbot for Basque, was created. It was later improved in a second version. As part of the “kAIxo” project (the Basque “kaixo” corresponds to the English “hello”), the chatbot kAIxo was built, which speaks Basque. Its purpose is to keep users practicing written or spoken language or to develop the desire to learn the endangered language. The chatbot is based on GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Flash, and the user can select his or her preferred large language model (LLM). Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG) plays a central role. The ChatSubs dataset is used, which contains subtitles of movie dialogs in Basque. Thanks to a text-to-speech engine, the chatbot can also speak. At the final presentation, Nicolas Lluis Araya presented a working prototype that can be accessed via www.kaixo.ch.
Role Player Nina
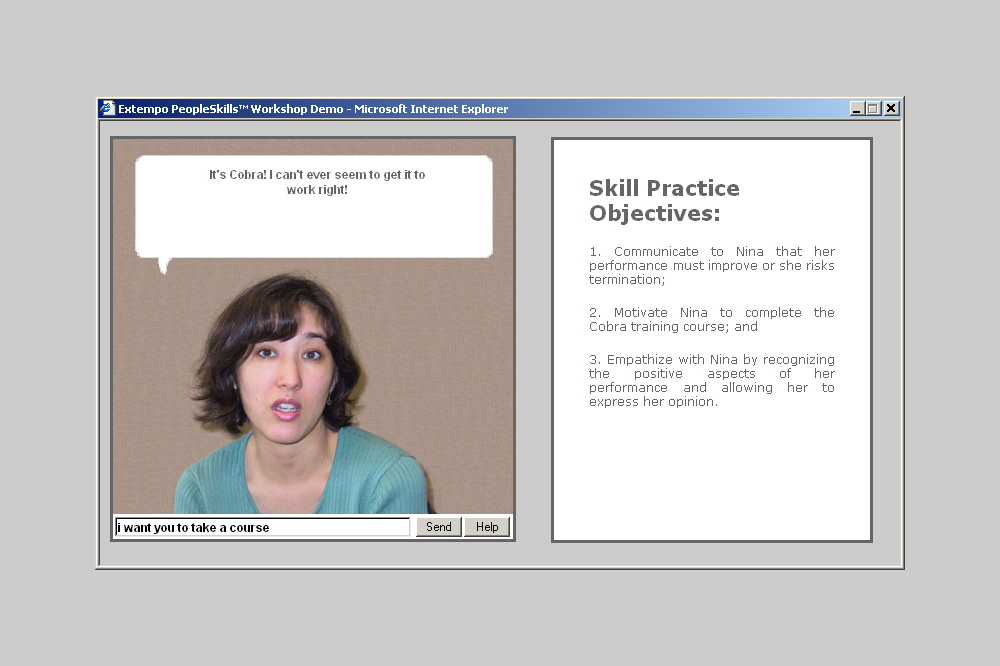
Around the turn of the millennium, there were already numerous pedagogical agents, i.e., chatbots, voice assistants, and early social robots in learning environments. Names such as Virtual Learning Companions (VLCs) were also commonly used for the purely virtual versions. One of the companies that was ahead of its time was Extempo Systems, Inc. based in Redwood City, California. The company had evolved out of the Stanford Engineering School and designed and developed commercial agents for entertainment, business, and education: “Extempo makes e-learning products that help corporate employees perfect their people skills. The company’s approach allows every learner to achieve mastery of the people skills they need for effective management, teamwork, sales, customer service, and other critical business functions. Extempo’s products give learners authentic practice in a variety of job-specific conversational role-plays, along with expert individualized coaching throughout the learning process.” (Extempo Systems) One example was the virtual Nina, with whom you could communicate and who you were supposed to motivate to behave in a certain way. It wasn’t just the functionality that was impressive at the time, but also the design of the characters.
The kAIxo Project
The interim presentation of the kAIxo project took place on 11 November 2024. Nicolas Lluis Araya is the project collaborator. Chatbots for dead, endangered, and extinct languages are being developed at the FHNW School of Business. One well-known example is @llegra, a chatbot for Vallader. Oliver Bendel recently tested the reach of GPTs for endangered languages such as Irish (Irish Gaelic), Maori, and Basque. According to ChatGPT, there is a relatively large amount of training material available for them. On 12 May 2024 – after Irish Girl and Maori Girl – a first version of Adelina, a chatbot for Basque, was created. It was later improved in a second version. As part of the “kAIxo” project (the Basque “kaixo” corresponds to the English “hello”), the chatbot or voice assistant kAIxo is being built to speak Basque. Its purpose is to keep users practising written or spoken language or to develop the desire to learn the endangered language. The chatbot is based on GPT-4o. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a central role. A ChatSubs dataset is used, which contains dialogues in Spanish and three other official Spanish languages (Catalan, Basque, and Galician). Nicolas Lluis Araya presented a functioning prototype at the interim presentation. This is now to be expanded step by step.
AI Ethics at the FHNW
Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel has been teaching information ethics, AI ethics, robot ethics, and machine ethics at the FHNW for around 15 years. He is responsible for the “Ethik und Technologiefolgenabschätzung” (“Ethics and Technology Assessment”) module in the new Business AI degree program at the FHNW School of Business in Olten. Here, the focus is on AI ethics, but students will also learn about robot ethics and machine ethics approaches – including annotated decision trees and moral prompt engineering. And they will use information ethics, including data ethics, to analyze and evaluate the origins and flows of data and information and engage in bias discussions. Last but not least, they will delve into technology assessment. Oliver Bendel also teaches the “Ethik und Recht” (“Ethics and Law”) module in the Business Information Systems degree program at the FHNW School of Business in Olten (which he took over in 2010 as “Informatik, Ethik und Gesellschaft”, later renamed “Informationsethik”), the “Recht und Ethik” (“Law and Ethics”) module in the Geomatics degree program at the FHNW School of Architecture, Construction and Geomatics in Muttenz, and “Ethisches Reflektieren” (“Ethical Reflecting”) and “Ethisches Implementieren” (“Ethical Implementing”) in the Data Science degree program at the FHNW School of Engineering in Brugg-Windisch. His elective modules on social robotics are very popular (Photo: Pati Grabowicz).
Continuation of the AAAI Spring Symposia
On 27 August 2024, AAAI announced the continuation of the AAAI Spring Symposium Series, to be held March 31 – April 2, 2025, at San Francisco Airport Marriott Waterfront in Burlingame, CA. The Call for Proposals for the Spring Symposium Series is available on the Spring Symposium Series website. According to the organizers, proposals are due October 4, 2024, and early submissions are encouraged. “The Spring Symposium Series is an annual set of meetings run in parallel at a common site. It is designed to bring colleagues together in an intimate forum while at the same time providing a significant gathering point for the AI community.” (Website AAAI) The traditional conference will therefore not be held at Stanford University in 2025 – as it was in 2023. It returned there in 2024 to the delight of all participants. The Covid-19 pandemic had hit the conference hard before. The AAAI can only be advised to return to Stanford in 2026. Only there will the conference live up to its promise.